Abscesses of the Periodontium
1. Overview of Periodontal abscess
A. Introduction in the Periodontal abscess
1. Periodontal abscess can be defined as an acute infection with the participation of a limited collection of pus in the periodontium.
2. Abscesses periodontal collection of pus. Pus consists mainly of dead white blood cells that can result when the protective mechanisms of the body are involved in attempts to control the infection.
3. In its early stages, periodontal abscess can be found hygienist during oral inspection for planned treatment visit, but in the later stages of periodontal abscess may cause patients to a dentist for pain relief.
4. Abscesses periodontal described as limited. The term " limited means a localized abscess or confined to a specific site (i.e., the front surface of a tooth). Figure 33-1 shows a typical example of periodontal abscess.
5. Accurate bacterial etiology periodontal abscess is not clear, but it is known that most of these lesions contain microflora are mainly gram-negative and anaerobic.
Most studies indicate that bacteria have seen in these abscesses similar to bacteria saw in periodontitis patients with deeper pockets.
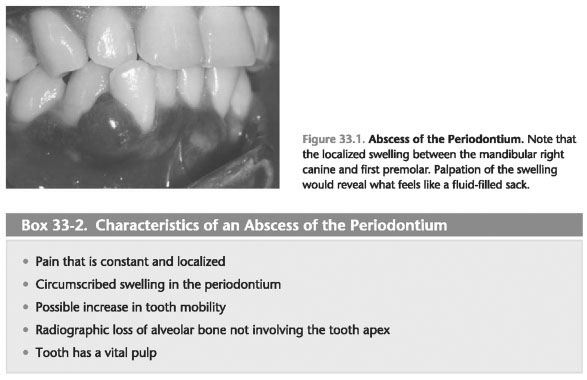 Characteristics of an Abscess of the Periodontium
Characteristics of an Abscess of the Periodontium
1. The typical patient complaints related to periodontal abscess include dental pain and swelling of the gums (box 33-2).
a. Pain as a result of periodontal abscess is usually described by the patient as constant pain. Patients are often report that the pain is easy for them to localize (i.e., the patient can specify the exact place that hurts).
B. In addition to the pain and swelling, the patient may report difficulty in chewing and may report, unpleasant taste in the mouth.
2. Oral examination, as a rule, will be to identify the presence of limited swelling of the soft tissues. This tumor can lead to gum only, or it may include both the gums and mucous.
3. Many teeth with periodontal abscess are also temporary increase mobility.
4. Dental x-rays of teeth with periodontal abscess often show bone loss in alveolar region abscess, but not with the participation of the top of the tooth. Fig. 33-2 is an x-ray of tooth abscess and periodontitis.
a. Alveolar bone loss due to periodontal abscess can happen very quickly when compared to the rate of the alveolar bone loss associated, as a rule, with the use of all forms of periodontitis.
B. Although dental x-ray of periodontal abscess can detect bone loss alveolar, periodontitis patient's impossible to say which part of the missing bones in the result of acute infection and the fact that part of the missing bone was called chronic periodontitis that existed prior formed an abscess...